
Mario Antonelli
Collected Works
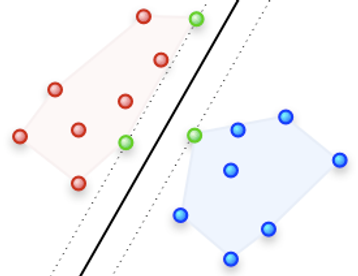
Decomposition Technique For Support Vector Machines
This software implents a binary support vector machine classifier [1,2].
A decomposition technique [3] is used to split the whole quadratic programming (QP) problem into a sequence of smaller QP sub-problems; the dimension NC of the subproblems can be chosen by the user and range from 10 to 300. To solve the quadratic programming (QP) sub-problem a non-monotone projected gradient is used [4].
In this algorithm, a different SVM formulation is adopted [5]; the dual of this formulation becomes a simpler bound-constrined problem.
A caching strategies is used to avoid the re-computation of the kernel function. The user can define the cache dimension in MB.
References:
-
Cristianini, N., Shawe-Taylor, J: "An Introduction to Support Vector Machines", Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 2000. http://www.support-vector.net
-
Kecman, V: "Learning and Soft Computing", MIT Press, Cambridge, MA. 2001.
-
J.C. Platt: "A Fast Algorithm for Training Support Vector Machines", Advances in Kernel Methods - Support Vector Learning, MIT Press, 1998.
-
M. Antonelli, A. Rizzi: "A Non-Monotone Optimization Algorithm for IIR Filter Design", Univ. of Rome La Sapienza, Rome.
-
CHIH-WEI HSU CHIH-JEN LIN: "Simple Decomposition Method for Support Vector Machines", Machine Learning, 46, 291–314, 2002 Kluwer Academic Publishers.